Difference between revisions of "Goerz"
(→Sources: commenting out a photo to which all rights are reserved) |
(various) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Flickr_image | {{Flickr_image | ||
| − | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/89864432@N00/2799828535/in/pool- | + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/89864432@N00/2799828535/in/pool-camerawiki |
|image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3233/2799828535_9c522e74fa.jpg | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3233/2799828535_9c522e74fa.jpg | ||
|image_align= right | |image_align= right | ||
|image_text= | |image_text= | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''C. P. Goerz''' was founded in 1886 by Carl Paul Goerz (1854-1923), a salesman who once had been in apprenticeship at [[Emil Busch]] in Rathenow and later was partner of [[E. Krauss|Eugen Krauss]] in Paris. Originally Goerz sold mathematical tools for schools, | + | '''C. P. Goerz''' was founded in 1886 by Carl Paul Goerz (1854-1923), a salesman who once had been in apprenticeship at [[Emil Busch]] in Rathenow and later was partner of [[E. Krauss|Eugen Krauss]] in Paris. Originally Goerz sold mathematical tools for schools, but from 1887 he added cameras. By taking over F. A. Hintze's workshop in 1888 his company started to make cameras, and was named '''Optische Anstalt C. P. Goerz''' from 1890. It was based in Berlin-Friedenau. In 1888 Goerz employed the engineer Carl Moser (1858-1892) and the optician Karl Hertel to start the development of lenses. |
| − | Goerz is known primarily for ''Anschütz'' cameras, for ''Doppel-Anastigmat'', ''Hypergon'', ''Artar'', ''Pantar'', ''Tenaxiar'', ''Tenastigmat'', ''Hypar'', ''Hycon'', ''Certar'', ''Gotar'', ''Frontar'', ''Dialyt'', ''Syntor'', ''Celor'', ''Kalostigmat'', ''Paraplanat'', ''Choroskop'', ''Lynkeioskop'', ''Dogmar'' and | + | Goerz is known primarily for ''Anschütz'' cameras, for ''Doppel-Anastigmat'', ''Hypergon'', ''Artar'', ''Pantar'', ''Tenaxiar'', ''Tenastigmat'', ''Hypar'', ''Hycon'', ''Certar'', ''Gotar'', ''Frontar'', ''Dialyt'', ''Syntor'', ''Celor'', ''Kalostigmat'', ''Paraplanat'', ''Choroskop'', ''Lynkeioskop'', ''Dogmar'' and ''[[Dagor]]'' camera lenses , and for ''Tengor'' and ''[[Tenax]]'' cameras, later continued by [[Zeiss Ikon]]. Specialties of Goerz were the cameras with "rouleau-shutter" since the company had the exclusive right to produce the fast [[focal plane shutter]] (1/1000sec.) that Ottomar Anschütz (1846-1907) had invented in 1883. These were mainly, but not exclusively, strut folding cameras, known as Ottomar Anschütz or Goerz Anschütz cameras, and many branded [[Goerz Anschütz Ango|Ango]] as abbreviation for Anschütz and Goerz. The first one was the Goerz-Anschütz-Moment-Apparat of 1890, a box camera for 9×12cm plates with a good lens mounted on the front plate. |
| − | Other products of Goerz were meteorological and aeronautical instruments, binoculars and ''Alethar'' repro lenses, gun scopes and another camera shutter, the ''Sector'' | + | Other products of Goerz were meteorological and aeronautical instruments, binoculars and ''Alethar'' repro lenses, gun scopes and another camera shutter, the ''Sector''. In 1903 it founded a department for military optics which became the world's largest military optics maker. Another big success was the making of scientific telescopes. A telescope for viewing a total eclipse and a three-color projector were made for the famous [[Dr. Adolf Miethe]]. |
| − | In 1895 Goerz founded a branch in New York that started own production in 1902 and was to become the C. P. Goerz American Optical Co. in 1905 (see [[Serial_numbers | here]] for dating these serial numbers). This company continued to operate independently in the US until 1972. Until WWI many great companies cooperated with Goerz. [[Rochester Optical Co.]] used Goerz lenses for its [[Snappa Camera]] in 1902, [[Kodak]] for its ''No. 3 Folding Pocket Kodak'' in 1901, and [[Ross]] in London got a license to make ''Dagor'' double [[anastigmat]] lenses already in 1893. | + | In 1895 Goerz founded a branch in New York that started its own production in 1902 and was to become the C. P. Goerz American Optical Co. in 1905 (see [[Serial_numbers | here]] for dating these serial numbers). This company continued to operate independently in the US until 1972. Until WWI many great companies cooperated with Goerz. [[Rochester Optical Co.]] used Goerz lenses for its [[Snappa Camera]] in 1902, [[Kodak]] for its ''No. 3 Folding Pocket Kodak'' in 1901, and [[Ross]] in London got a license to make ''Dagor'' double [[anastigmat]] lenses already in 1893. |
| − | In 1903 Goerz | + | In 1903 Goerz went public. In 1908, Goerz Photochemisches Werk GmbH was founded in Berlin-Zehlendorf. This company produced roll film and film for the movie industry. In 1910 Goerz became owner of the Sendlinger Optische Glaswerke, an [[optical glass]] maker near Munich. At that time the company had further factories in Berlin-Friedenau, Vienna, Pressburg (present-day Bratislava), New York and Winterstein. It had offices in Berlin-Friedenau, Paris, London and New York. |
| − | During the First World War, Goerz's main production was making optical instruments for the German and Austrian military, but started | + | During the First World War, Goerz's main production was making optical instruments for the German and Austrian military, but it also started making electrical searchlights. After the war further making of military equipment was forbidden by the Peace Treaty of Versailles. The company tried to make mechanical calculators and other scientific instruments instead but failed to regain its former success. |
{{Berlin}} | {{Berlin}} | ||
| − | In 1926 the German branch of Goerz was saved from bankruptcy by being merged with [[ICA]], [[Contessa-Nettel]] and [[Ernemann]] to form [[Zeiss Ikon]]. This had major consequences for the company; the [[Carl Zeiss]] company held a majority stake | + | In 1926 the German branch of Goerz was saved from bankruptcy by being merged with [[ICA]], [[Contessa-Nettel]] and [[Ernemann]] to form [[Zeiss Ikon]]. This had major consequences for the company; the [[Carl Zeiss]] company held a majority stake and demanded that the other firms end their lens production. This was the end of the famed [[Dagor]] lenses, at least in Europe. An [[Goerz (Austria)|Austrian branch of C. P. Goerz]] was still active in the 1950s, introducing an astonishing little subminiature reflex camera with six-element Helgor lens, the [[Minicord]]. |
{{br}} | {{br}} | ||
== Cameras == | == Cameras == | ||
{{Flickr_image | {{Flickr_image | ||
| − | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/89864432@N00/1467048454/in/pool- | + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/89864432@N00/1467048454/in/pool-camerawiki/ |
|image= http://farm2.static.flickr.com/1260/1467048454_739c620908_m.jpg | |image= http://farm2.static.flickr.com/1260/1467048454_739c620908_m.jpg | ||
|image_align= right | |image_align= right | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
}} --> | }} --> | ||
=== Literature === | === Literature === | ||
| − | * C.P. Goerz & Cie. , "C. P. GOERZ 1886-1911 - Oesterr.-Ung. Optische Anstalt C. P. Goerz Gesellschaft m.b.H", Vienna 1912 | + | * C.P. Goerz & Cie., "C. P. GOERZ 1886-1911 - Oesterr.-Ung. Optische Anstalt C. P. Goerz Gesellschaft m.b.H", Vienna 1912 |
=== Links === | === Links === | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
* [http://photo.even.free.fr/col_app_goerz.php Goerz page] at [http://photo.even.free.fr/ Collection G. Even's site] | * [http://photo.even.free.fr/col_app_goerz.php Goerz page] at [http://photo.even.free.fr/ Collection G. Even's site] | ||
* [http://www.bolexcollector.com/lenses/40goerz.html C.P. Goerz American Optical Co.] company history and list of cine lenses | * [http://www.bolexcollector.com/lenses/40goerz.html C.P. Goerz American Optical Co.] company history and list of cine lenses | ||
| − | * [http://www2f.biglobe.ne.jp/~ter-1212/sakura/dagor.htm Double-Anastigmat, Dagor and Pantar] lenses as well as [http://www2f.biglobe.ne.jp/~ter-1212/sakura/celor.htm Syntor and Celor] lenses on Japanese | + | * [http://www2f.biglobe.ne.jp/~ter-1212/sakura/dagor.htm Double-Anastigmat, Dagor and Pantar] lenses as well as [http://www2f.biglobe.ne.jp/~ter-1212/sakura/celor.htm Syntor and Celor] lenses on Japanese website about R. Konishi Rokuoh-Sha [http://www2f.biglobe.ne.jp/~ter-1212/sakura/] |
* [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/general/html/liste5_imagettes.php#goerz_berlin Goerz] at www.collection-appareils.fr | * [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/general/html/liste5_imagettes.php#goerz_berlin Goerz] at www.collection-appareils.fr | ||
** Goerz pages [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/pp_1913/html/page_8.php], [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/pp_1913/html/page_9.php] in Henri Plait catalogue 1913 [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/pp_1913/html/catalogue1913.php] | ** Goerz pages [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/pp_1913/html/page_8.php], [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/pp_1913/html/page_9.php] in Henri Plait catalogue 1913 [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/pp_1913/html/catalogue1913.php] | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 9 April 2011

|
C. P. Goerz was founded in 1886 by Carl Paul Goerz (1854-1923), a salesman who once had been in apprenticeship at Emil Busch in Rathenow and later was partner of Eugen Krauss in Paris. Originally Goerz sold mathematical tools for schools, but from 1887 he added cameras. By taking over F. A. Hintze's workshop in 1888 his company started to make cameras, and was named Optische Anstalt C. P. Goerz from 1890. It was based in Berlin-Friedenau. In 1888 Goerz employed the engineer Carl Moser (1858-1892) and the optician Karl Hertel to start the development of lenses.
Goerz is known primarily for Anschütz cameras, for Doppel-Anastigmat, Hypergon, Artar, Pantar, Tenaxiar, Tenastigmat, Hypar, Hycon, Certar, Gotar, Frontar, Dialyt, Syntor, Celor, Kalostigmat, Paraplanat, Choroskop, Lynkeioskop, Dogmar and Dagor camera lenses , and for Tengor and Tenax cameras, later continued by Zeiss Ikon. Specialties of Goerz were the cameras with "rouleau-shutter" since the company had the exclusive right to produce the fast focal plane shutter (1/1000sec.) that Ottomar Anschütz (1846-1907) had invented in 1883. These were mainly, but not exclusively, strut folding cameras, known as Ottomar Anschütz or Goerz Anschütz cameras, and many branded Ango as abbreviation for Anschütz and Goerz. The first one was the Goerz-Anschütz-Moment-Apparat of 1890, a box camera for 9×12cm plates with a good lens mounted on the front plate.
Other products of Goerz were meteorological and aeronautical instruments, binoculars and Alethar repro lenses, gun scopes and another camera shutter, the Sector. In 1903 it founded a department for military optics which became the world's largest military optics maker. Another big success was the making of scientific telescopes. A telescope for viewing a total eclipse and a three-color projector were made for the famous Dr. Adolf Miethe.
In 1895 Goerz founded a branch in New York that started its own production in 1902 and was to become the C. P. Goerz American Optical Co. in 1905 (see here for dating these serial numbers). This company continued to operate independently in the US until 1972. Until WWI many great companies cooperated with Goerz. Rochester Optical Co. used Goerz lenses for its Snappa Camera in 1902, Kodak for its No. 3 Folding Pocket Kodak in 1901, and Ross in London got a license to make Dagor double anastigmat lenses already in 1893.
In 1903 Goerz went public. In 1908, Goerz Photochemisches Werk GmbH was founded in Berlin-Zehlendorf. This company produced roll film and film for the movie industry. In 1910 Goerz became owner of the Sendlinger Optische Glaswerke, an optical glass maker near Munich. At that time the company had further factories in Berlin-Friedenau, Vienna, Pressburg (present-day Bratislava), New York and Winterstein. It had offices in Berlin-Friedenau, Paris, London and New York.
During the First World War, Goerz's main production was making optical instruments for the German and Austrian military, but it also started making electrical searchlights. After the war further making of military equipment was forbidden by the Peace Treaty of Versailles. The company tried to make mechanical calculators and other scientific instruments instead but failed to regain its former success.
| Camera industry in Berlin |
| Agfa | Amigo | Astro Berlin | Bermpohl | Bopp | B+W | Foth | Goerz | Grass & Worff | Levy-Roth | Ernst Lorenz | Plasmat | Rudolph | Rothgiesser & Schlossmann | Rüdersdorf | Schulze & Billerbeck | Sida | Stegemann | Romain Talbot |
In 1926 the German branch of Goerz was saved from bankruptcy by being merged with ICA, Contessa-Nettel and Ernemann to form Zeiss Ikon. This had major consequences for the company; the Carl Zeiss company held a majority stake and demanded that the other firms end their lens production. This was the end of the famed Dagor lenses, at least in Europe. An Austrian branch of C. P. Goerz was still active in the 1950s, introducing an astonishing little subminiature reflex camera with six-element Helgor lens, the Minicord.
Contents
Cameras
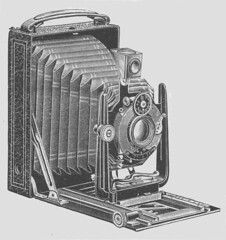
|
| Manufok-Tenax |
- Goerz-Anschütz-Moment-Apparat
- Ango
- Plate Tenax (Vest Pocket Tenax)
- Pocket Tenax
- Roll-Tenax
- Rollfilm Tenax
- Taro Tenax
- Manufok-Tenax
- Stereotenax
- Stereo-Pocket-Tenax
- Goerz-Anschütz Stereo-Klapp-Camera
- Roll-Tengor
- Box-Tengor
- Piccolissima
- Universal-Reise-Camera Insuperabilis
- Spezial-Ballon-Camera
- Jagd-Reflex-Ango
Shutters
- Goerz-Anschütz rouleau shutter
- Goerz Sektoren-Verschluss
Sources
Literature
- C.P. Goerz & Cie., "C. P. GOERZ 1886-1911 - Oesterr.-Ung. Optische Anstalt C. P. Goerz Gesellschaft m.b.H", Vienna 1912
Links
- Goerz-Anschütz-Moment-Apparat at www.ottomar-anschuetz.de [1]
- a company history in German on wikipedia.org
- Goerz lens catalog from 1916
- Goerz page at Collection G. Even's site
- C.P. Goerz American Optical Co. company history and list of cine lenses
- Double-Anastigmat, Dagor and Pantar lenses as well as Syntor and Celor lenses on Japanese website about R. Konishi Rokuoh-Sha [2]
- Goerz at www.collection-appareils.fr
- Goerz Rollfilm Tenax and Roll-Tenax variants at Westlicht
- Goerz on www.collection-appareils.com by Sylvain Halgand