Difference between revisions of "Tessar"
Danipuntocom (talk | contribs) m (Added link about repairing a Tessar) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Flickr_image | {{Flickr_image | ||
| − | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/ | + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/89864432@N00/5014656415/in/pool-camerapedia |
| − | |image= http:// | + | |image= http://farm5.static.flickr.com/4132/5014656415_8948fa7dca_m.jpg |
|image_align=right | |image_align=right | ||
| − | |image_text= | + | |image_text=original Tessar from [[Zeiss]] collection |
}} | }} | ||
The '''Tessar''' is a camera [[lens]] designed by Dr. Paul Rudolph, working for the [[Carl Zeiss]] Jena company, in 1902. It is normally used as a standard lens, and versions of it have been fitted to many millions of cameras. | The '''Tessar''' is a camera [[lens]] designed by Dr. Paul Rudolph, working for the [[Carl Zeiss]] Jena company, in 1902. It is normally used as a standard lens, and versions of it have been fitted to many millions of cameras. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|image_align= left | |image_align= left | ||
|image_text= Cut-away diagram of a Tessar | |image_text= Cut-away diagram of a Tessar | ||
| − | }} | + | }}<br style="clear:left"/> |
{{Flickr_image | {{Flickr_image | ||
| − | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/ | + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/24225011@N04/2763351439/in/pool-camerapedia/ |
| − | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/ | + | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3177/2763351439_b1d7644715_m.jpg |
| − | |image_align= right | + | |image_align=right |
| − | |image_text= Tessar on [[ | + | |image_text=Cross-section of a 50mm f2.8 Tessar,<br>with front element on the left.<BR>(for 35mm, [[M42]] fitting) |
}} | }} | ||
The original design had a maximum aperture of f/6.3, but the developments in design allowed f/2.8 by 1930. | The original design had a maximum aperture of f/6.3, but the developments in design allowed f/2.8 by 1930. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
In addition to production by [[Carl Zeiss]], the Tessar name and design (under license) was used in the production of numerous lenses by [[Bausch & Lomb]] (Rochester), [[Ross]] (London) and [[Krauss]] (Paris). | In addition to production by [[Carl Zeiss]], the Tessar name and design (under license) was used in the production of numerous lenses by [[Bausch & Lomb]] (Rochester), [[Ross]] (London) and [[Krauss]] (Paris). | ||
| − | The Tessar design has been widely copied by nearly all major optics companies. | + | The Tessar design has been widely copied by nearly all major optics companies. |
| + | |||
| + | A very partial list includes: | ||
* [[Agfa]] Solinar | * [[Agfa]] Solinar | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
* [[FED]]/[[KMZ]] [[Industar]] | * [[FED]]/[[KMZ]] [[Industar]] | ||
* [[Ilex]] Paragon | * [[Ilex]] Paragon | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/mario_groleau/2986071602/in/pool-camerapedia | ||
| + | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3039/2986071602_09b0711135_m.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= right | ||
| + | |image_text= Tessar on [[Ikonta]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
* [[Kodak]] Ektar | * [[Kodak]] Ektar | ||
* [[Konica]] Macro-Hexanon AR 55 mm f/3.5 | * [[Konica]] Macro-Hexanon AR 55 mm f/3.5 | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 22 September 2010

|
| original Tessar from Zeiss collection |
The Tessar is a camera lens designed by Dr. Paul Rudolph, working for the Carl Zeiss Jena company, in 1902. It is normally used as a standard lens, and versions of it have been fitted to many millions of cameras.
The design consists of four elements in three groups; the front element is positive, bi-convex (with the rear almost flat), the central a negative bi-concave and, following an aperture, at the rear is a cemented doublet of plano-concave and a bi-convex elements. Though often referred to as a "modified Cooke triplet", the Tessar is actually a development of Rudolph's 1899 Unar (4 element in 4 groups) lens, itself a development of Rudolph's 1890 Zeiss Anastigmat (4 elements in 2 groups) lens.

|
| Cut-away diagram of a Tessar |
|
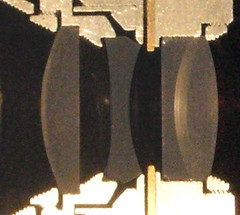
| Cross-section of a 50mm f2.8 Tessar, with front element on the left. (for 35mm, M42 fitting) |
The original design had a maximum aperture of f/6.3, but the developments in design allowed f/2.8 by 1930.
In addition to production by Carl Zeiss, the Tessar name and design (under license) was used in the production of numerous lenses by Bausch & Lomb (Rochester), Ross (London) and Krauss (Paris).
The Tessar design has been widely copied by nearly all major optics companies.
A very partial list includes:
- Agfa Solinar
- Asahi/Pentax Macro-Takumar 50mm f/4
- Bausch & Lomb Tessar (under license)
- Canon 38mm FLP, 50mm f/2.8 and f/3.5 RF lenses, 50mm FL f/3.5
- Dallmeyer Dalmac, Perfac, Serrac
- Ernemann Ernon
- FED/KMZ Industar
- Ilex Paragon

|
| Tessar on Ikonta |
- Kodak Ektar
- Konica Macro-Hexanon AR 55 mm f/3.5
- Krauss-Zeiss Tessar (under license)
- Leitz Elmar
- Mamiya Press lenses - 100mm f/3.5, 127mm f/4.7, 150mm f/5.6
- Meyer Primotar
- Minolta Rokkor TLR
- Minox Minoxar
- Nikon 45mm GN Nikkor, El-Nikkor 50mm f/4
- Olympus in many of their compact cameras including the Trip 35 (40mm f/2.8) and mju series.
- Plaubel Anticomar
- Rodenstock Ysar, Rogonar
- Ross Xtralux
- Ross Tessar (under license)
- Schneider Xenar, Comparon
- Taylor & Hobson Apotal, Ental
- Voigtlander Heliostigmat, Skopar
- Wollensak Raptar
- Yashica Yashinon TLR
Sources
- Rudolf Kingslake, A History of the Photographic Lens, Academic Press, 1989