Difference between revisions of "Topogon"
(Created page with "{{Flickr_image |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/heritagefutures/6368541301/in/pool-camerawiki |image= http://farm7.staticflickr.com/6116/6368541301_5f8635d8aa.jpg |ima...") |
m (fixing Flickr bug--missing period in image URL) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Flickr_image | {{Flickr_image | ||
|image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/heritagefutures/6368541301/in/pool-camerawiki | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/heritagefutures/6368541301/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| − | |image= http://farm7. | + | |image= http://farm7.static.flickr.com/6116/6368541301_5f8635d8aa.jpg |
|image_align= right | |image_align= right | ||
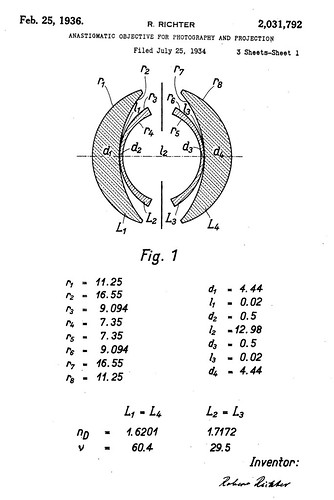
|image_text= Robert Richter Patent for the Topogon | |image_text= Robert Richter Patent for the Topogon | ||
Revision as of 16:15, 20 November 2011
|
| Robert Richter Patent for the Topogon image by Dirk HR Spennemann (Image rights) |
The Topogon is an extra-wide field photographic lens of a double-Gauss design with an extremely curved meniscus to provide a 90° field of view. The lens is symmetrical front to back. The two outer positive elements are of high index crown glass while the two inner negative elements are of a high index flint glass. The lens was designed in 1933 by Robert Richter for Carl Zeiss, Jena.[1] In the U.S.A. the lens was copied by Bausch & Lomb and sold as the Metrogon, which found widespread use in aerial cameras.