Topogon
|
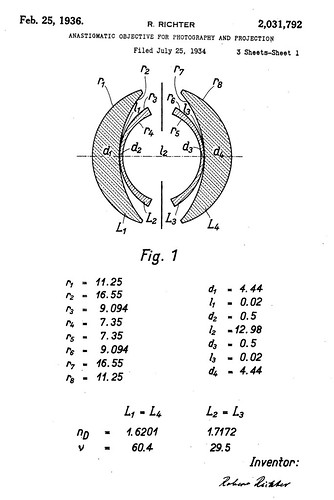
| Robert Richter Patent for the Topogon image by Dirk HR Spennemann (Image rights) |
The Topogon is an extra-wide field photographic lens of a double-Gauss design with an extremely curved meniscus to provide a 90° field of view. The lens is symmetrical front to back. The two outer positive elements are of high index crown glass while the two inner negative elements are of a high index flint glass. The lens was designed in 1933 by Robert Richter for Carl Zeiss, Jena.[1] In the U.S.A. the lens was copied by Bausch & Lomb and sold as the Metrogon, which found widespread use in aerial cameras.