Difference between revisions of "CCD"
(note on multi-CCD/interpolation) |
m (grammar, link > resolution) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | A '''CCD''' or ''Charge-Coupled Device'' is an analog electronic device that can be used as the image sensor in place of film in an electronic camera or scanner. Many [[digital camera]]s use CCDs as their image sensor, although some use CMOS or other devices instead. The CCD was invented in 1969 at Bell Labs by Willard Boyle and George Smith. Whilst the CCD is sensitive to light - and so can be used as an image sensor, it has also been used as a memory device. Some early cameras (e.g. [[Minolta RD-175]]) used more than one CCD - with a colour-separation prism or filter directing different colours of light to the individual sensors. | + | A '''CCD''' or ''Charge-Coupled Device'' is an analog electronic device that can be used as the image sensor in place of film in an electronic camera or scanner. Many [[digital camera]]s use CCDs as their image sensor, although some use CMOS or other devices instead. The CCD was invented in 1969 at Bell Labs by Willard Boyle and George Smith<ref>[http://www.bell-labs.com/news/1999/september/20/1.html Bell Labs article on invention of CCDs]</ref>. Whilst the CCD is sensitive to light - and so can be used as an image sensor, it has also been used as a memory device. Some early cameras (e.g. [[Minolta RD-175]]) used more than one CCD - with a colour-separation prism or filter directing different colours of light to the individual sensors. |
{{Flickr image | {{Flickr image | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}}{{br}} | }}{{br}} | ||
| − | The resolution of the image sensor governs the resolution of the camera, although some cameras can produce increased [[pixel]] counts using interpolation software - particularly with multi-CCD sensors. | + | The [[resolution]] of the image sensor governs the resolution of the camera, although some cameras can produce increased [[pixel]] counts using interpolation software - particularly with multi-CCD sensors. |
===CCD makers=== | ===CCD makers=== | ||
| − | Many of the big camera makers or consumer electronics companies have | + | Many of the big camera makers or consumer electronics companies have their own CCD production facility, for example [[Sony]] and [[Fujifilm]]. Other companies specialise in making camera sensors, among them |
*[[Dalsa]] | *[[Dalsa]] | ||
and | and | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| − | + | <references /> | |
| + | |||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charge-coupled_device CCD on Wikipedia] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charge-coupled_device CCD on Wikipedia] | ||
Revision as of 13:14, 17 May 2008
A CCD or Charge-Coupled Device is an analog electronic device that can be used as the image sensor in place of film in an electronic camera or scanner. Many digital cameras use CCDs as their image sensor, although some use CMOS or other devices instead. The CCD was invented in 1969 at Bell Labs by Willard Boyle and George Smith[1]. Whilst the CCD is sensitive to light - and so can be used as an image sensor, it has also been used as a memory device. Some early cameras (e.g. Minolta RD-175) used more than one CCD - with a colour-separation prism or filter directing different colours of light to the individual sensors.
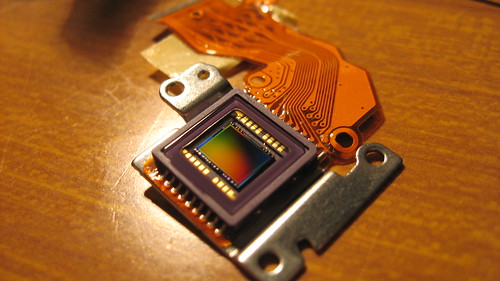
|
| 3.2 megapixel CCD device of a Canon A75 digital compact camera |
The resolution of the image sensor governs the resolution of the camera, although some cameras can produce increased pixel counts using interpolation software - particularly with multi-CCD sensors.
CCD makers
Many of the big camera makers or consumer electronics companies have their own CCD production facility, for example Sony and Fujifilm. Other companies specialise in making camera sensors, among them
and