Difference between revisions of "Richard (Jules)"
Camerawiki (talk | contribs) |
m (lenses) |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
{{French companies}} | {{French companies}} | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/27641890@N07/3262895356/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3399/3262895356_b4e758bc2c.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= left | ||
| + | |image_text= Jules Richard Vérascope,early 20th century model | ||
| + | |image_by= kek szakallu | ||
| + | |image_rights= with permission | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/27641890@N07/3262893186/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3347/3262893186_87915fbcf0_m.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= left | ||
| + | |image_text= Front view | ||
| + | |image_by= kek szakallu | ||
| + | |image_rights= with permission | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{br}} | ||
| + | {|class=floatright | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/27641890@N07/3262079953/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3332/3262079953_feb751d9c4.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= right | ||
| + | |image_text= Vérascope size compared to various 35mm cameras | ||
| + | |image_by= kek szakallu | ||
| + | |image_rights= with permission | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The instrument company owned by Jules Richard was a pioneer in [[stereo]] photography, popularizing a 45x107mm plate format which made very portable stereo cameras possible. | ||
| + | Jules Richard, its founder was an inventor and pioneer in several fields of engineering in the late 1800s France. He invented instruments that allowed recording (barometers) and by 1893 he introduced the '''45x107mm''' glass plate format for Stereo photography. <ref>[https://stereoscopyhistory.net/stereoscopes-stereo-cameras/jules-richard/] stereoscopyhistory.net</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jules Richard introduced the '''Vérascope''' brand, for a simple to use line of stereo cameras using the 45x107mm format, which at the time was considered compact, and allowed the production of compact and cheaper cameras with "magazines" that carried 10-12 plates and allowed the photographer to take more than 1 picture and brought stereo photography to the masses. Initial versions used fixed 54mm f/10 lenses that produced good images from 5m to infinity. Later versions used Zeiss Tessar lenses. | ||
| + | This was followed by a simpler version called '''Glyphoscope''' which doubled as a viewer. | ||
| + | These cameras used the 45x107mm glass plates initially but the line was later expanded to 6x13 and 7x13 plates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''Homéos''' was first made in 1914 and was the first stereo camera for 35mm film. <ref>{{McKeown12}} Page 821.</ref> A second revised model followed in 1920. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The name '''Vérascope''' Richard became well known for cameras, accessories and stereoscopes ('''Taxiphote''' revolving for parlors) and the name was carried into the 1950s with the [[Verascope f40]] (which was imported and sold in the US under the [[Busch]] brand). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The popularity of stereo photography and the success of '''Vérascope''' was followed by other companies such as [[ICA]], and [[Ernemann]] until the 1930s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= https://www.flickr.com/photos/90900361@N08/52992181231/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= https://live.staticflickr.com/65535/52992181231_ccabdfe74e.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= right | ||
| + | |image_text= Homéos <br><small>image by Genéve Friede</small> | ||
| + | |image_by= | ||
| + | |image_rights= wp | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
| − | * [http://photo.even.free.fr/col_app.php?type=richard&title=Richard Jules Richard page] at [http:// | + | * [http://photo.even.free.fr/col_app.php?type=richard&title=Richard Jules Richard page] at [http://www.collectiongeven.com/piwigo/ Collection G. Even's site] (in French) |
| + | * [https://web.archive.org/web/20190911201944/http://www.ignomini.com/photographica/stereophotovintage/richardnudes/richardnudes.html About Jules Richard] and [https://web.archive.org/web/20190806010058/http://www.ignomini.com/photographica/wtf/wtf.html Stereo Cameras] at Ignomini (archived) | ||
| + | *[https://stereoscopyhistory.net/stereoscopes-stereo-cameras/jules-richard/ Jules Richard] at [https://stereoscopyhistory.net/ Andre Ruiter's Stereoscopy history website] | ||
| + | * [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/general/html/listeQ_imagettes.php#Richard Cameras Richard] on [http://www.collection-appareils.fr/general/html/francais.php www.collection-appareils.fr] by Sylvain Halgand (in French) | ||
| + | * [https://www.butkus.org/chinon/verascope/verascope/verascope.htm Verascope instruction manual] at Butkus's Orphan Cameras | ||
| + | {{br}} | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/30622512@N06/3105056078/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= http://farm4.static.flickr.com/3264/3105056078_eb397703a0.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= right | ||
| + | |image_text= c.1920 Richard Verascope 3S | ||
| + | |image_by= photokristof | ||
| + | |image_rights= with permission | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/gatochy/730320579/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= http://farm2.static.flickr.com/1071/730320579_699cefde7b.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= left | ||
| + | |image_text= 1930 Portuguese advertisement | ||
| + | |image_by= Gatochy | ||
| + | |image_rights= with permission | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Flickr_image | ||
| + | |image_source= http://www.flickr.com/photos/90900361@N08/8379038479/in/pool-camerawiki | ||
| + | |image= http://farm9.staticflickr.com/8518/8379038479_d44ff60da5.jpg | ||
| + | |image_align= right | ||
| + | |image_text= Le Glyphoscope c.1905 | ||
| + | |image_by= Geoff Harrisson | ||
| + | |image_rights= wp | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[Category: Camera makers]] | [[Category: Camera makers]] | ||
| + | [[Category: 45x107 stereo]] | ||
[[Category: France]] | [[Category: France]] | ||
| + | [[Category:R]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Stereo]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:18, 28 January 2024
| French | () | |
|---|---|---|
| companies | ||
| AFR | Alsaphot | André and Lieutier | Angénieux | Arca Swiss | As de Trèfle | Atoms | Aubertin | Balcar | Bardin | Bauchet | Baudry | Bellieni | Berthiot | Boumsell | Boyer | Bronzavia | Cindo | Cord | Cornu | Coronet | Darlot | Demaria-Lapierre | Derogy | Faller | FAP | Fex | Français | Compagnie Française de Photographie | Gallus | Gaumont | Georges Paris | Girard | Gitzo | Goldstein | Héard & Mallinjod | Hermagis | Idam | Itier | Jousset | Joux | Kafta | Kinax | Kodak Pathé | Krauss | Lumière | Lund | Mackenstein | Manufrance | MAPED | Mazo | MFAP | MIOM | Mollier | Mundus | Olbia | Omega | OPL | Pierrat | Richard | Richard (Jules) | Roussel | Royer | SEM | Secam | SIAP | Soulé | Spirotechnique | Tiranty | Vergne | Zion (France) | ||
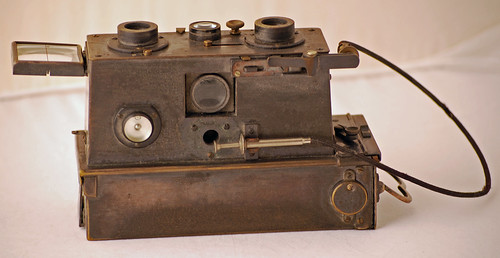
|
| Jules Richard Vérascope,early 20th century model image by kek szakallu (Image rights) |

|
| Front view image by kek szakallu (Image rights) |
|
The instrument company owned by Jules Richard was a pioneer in stereo photography, popularizing a 45x107mm plate format which made very portable stereo cameras possible. Jules Richard, its founder was an inventor and pioneer in several fields of engineering in the late 1800s France. He invented instruments that allowed recording (barometers) and by 1893 he introduced the 45x107mm glass plate format for Stereo photography. [1]
Jules Richard introduced the Vérascope brand, for a simple to use line of stereo cameras using the 45x107mm format, which at the time was considered compact, and allowed the production of compact and cheaper cameras with "magazines" that carried 10-12 plates and allowed the photographer to take more than 1 picture and brought stereo photography to the masses. Initial versions used fixed 54mm f/10 lenses that produced good images from 5m to infinity. Later versions used Zeiss Tessar lenses. This was followed by a simpler version called Glyphoscope which doubled as a viewer. These cameras used the 45x107mm glass plates initially but the line was later expanded to 6x13 and 7x13 plates.
The Homéos was first made in 1914 and was the first stereo camera for 35mm film. [2] A second revised model followed in 1920.
The name Vérascope Richard became well known for cameras, accessories and stereoscopes (Taxiphote revolving for parlors) and the name was carried into the 1950s with the Verascope f40 (which was imported and sold in the US under the Busch brand).
The popularity of stereo photography and the success of Vérascope was followed by other companies such as ICA, and Ernemann until the 1930s.

|
| Homéos image by Genéve Friede (Image rights) |
Notes
- ↑ [1] stereoscopyhistory.net
- ↑ McKeown, James M. and Joan C. McKeown's Price Guide to Antique and Classic Cameras, 12th Edition, 2005-2006. USA, Centennial Photo Service, 2004. ISBN 0-931838-40-1 (hardcover). ISBN 0-931838-41-X (softcover). Page 821.
Links
- Jules Richard page at Collection G. Even's site (in French)
- About Jules Richard and Stereo Cameras at Ignomini (archived)
- Jules Richard at Andre Ruiter's Stereoscopy history website
- Cameras Richard on www.collection-appareils.fr by Sylvain Halgand (in French)
- Verascope instruction manual at Butkus's Orphan Cameras

|
| c.1920 Richard Verascope 3S image by photokristof (Image rights) |

|
| 1930 Portuguese advertisement image by Gatochy (Image rights) |

|
| Le Glyphoscope c.1905 image by Geoff Harrisson (Image rights) |
